In the rapidly evolving field of healthcare, patient-centered care has emerged as a foundational philosophy that is reshaping the way care is delivered. At its core, patient-centered care emphasizes the importance of viewing the patient as a whole person, rather than just a set of symptoms or a medical condition. This approach prioritizes the patient's values, preferences, and needs, ensuring that they are active participants in their own healthcare journey. But what does patient-centered care truly mean, and what are the broader secondary effects of implementing this model in various healthcare settings?
Defining Patient-Centered Care
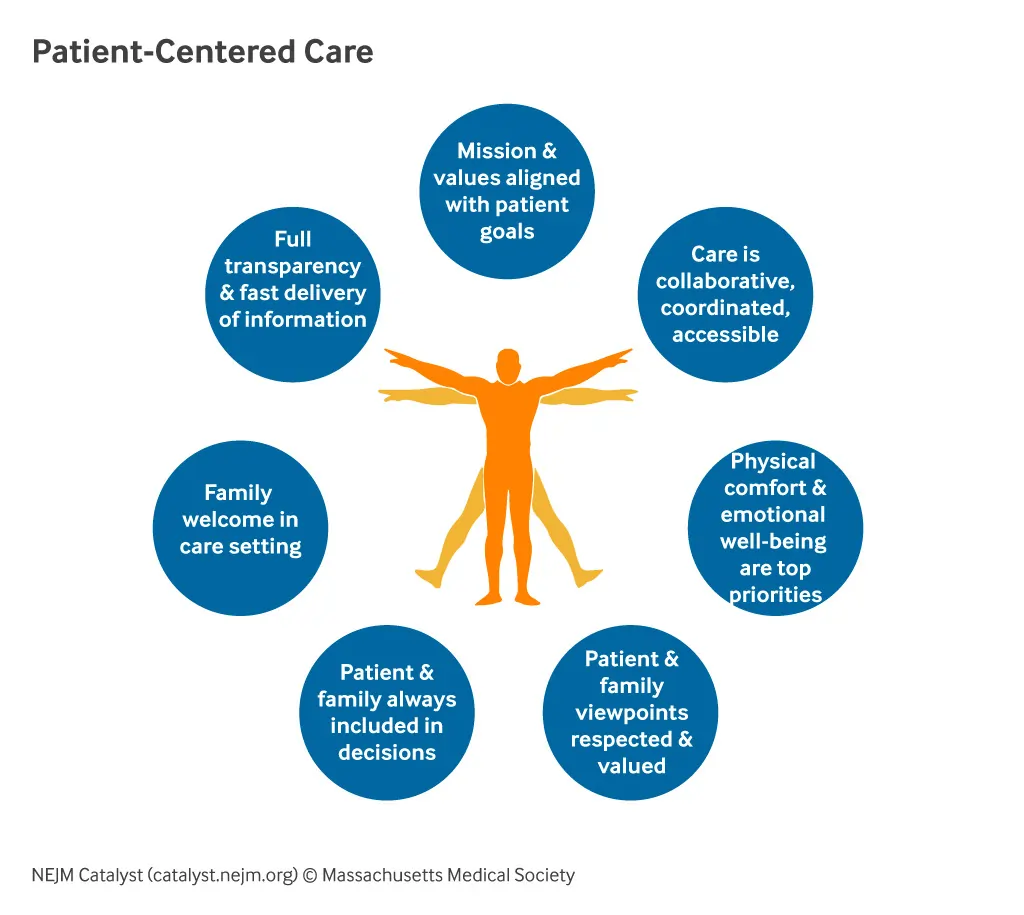
Patient-centered care is a holistic approach that prioritizes the patient’s experience and involvement in their care. This model of care revolves around the concept of respecting and responding to individual patient preferences, needs, and values, ensuring that these guide all clinical decisions. The goal is to foster a partnership between healthcare providers and patients, where open communication, empathy, and mutual respect are paramount.
The Institute of Medicine (IOM) has defined patient-centered care as “providing care that is respectful of and responsive to individual patient preferences, needs, and values, and ensuring that patient values guide all clinical decisions.” This definition underscores the importance of treating patients as partners in their care, rather than as passive recipients of medical interventions.
Key elements of patient-centered care include:
- Respect for Patient Values and Preferences: Recognizing that each patient has unique values, cultural backgrounds, and preferences, and incorporating these into care decisions.
- Coordinated and Integrated Care: Ensuring that care is organized across various healthcare settings and providers, so that patients experience seamless transitions and communication.
- Clear, High-Quality Information and Education: Providing patients with the information they need to make informed decisions about their care, delivered in a manner they can understand.
- Physical Comfort: Addressing physical comfort needs such as pain management, privacy, and hospital environment to enhance the overall care experience.
- Emotional Support: Offering psychological and emotional support to alleviate anxiety, fear, and other emotional challenges associated with illness and treatment.
- Involvement of Family and Friends: Recognizing the role of family and friends in the patient's care and involving them in decision-making processes when appropriate.
- Access to Care: Ensuring that patients have timely access to the care they need, including appointments, treatments, and information.
The Core Principles of Patient-Centered Care
1. Dignity and Respect
At the heart of patient-centered care is the principle of treating each patient with dignity and respect. This means acknowledging and honoring the patient’s individuality, cultural background, and personal preferences. Healthcare providers are encouraged to listen to patients actively, understand their concerns, and engage them in open, honest conversations about their health and treatment options.
Respecting patient autonomy is another crucial aspect of this principle. Patients should have the freedom to make decisions about their care, based on their values and preferences, even when these decisions differ from the recommendations of healthcare providers. By fostering an environment of mutual respect, patient-centered care empowers individuals to take an active role in their healthcare journey.
2. Collaboration and Partnership
Patient-centered care is built on the foundation of collaboration and partnership between patients, their families, and healthcare providers. This model encourages shared decision-making, where patients are involved in every step of the care process, from diagnosis to treatment and follow-up care. Healthcare providers act as guides, offering their expertise while also respecting the patient’s knowledge of their own body and life circumstances.
This collaborative approach not only enhances the patient’s experience but also leads to better health outcomes. Studies have shown that when patients are actively engaged in their care, they are more likely to adhere to treatment plans, report higher satisfaction levels, and experience improved overall health.
3. Holistic Care
Holistic care is another key principle of patient-centered care. Rather than focusing solely on the medical aspects of a patient’s condition, this approach considers the patient’s physical, emotional, social, and spiritual well-being. Healthcare providers are encouraged to look beyond symptoms and diagnoses to understand the broader context of a patient’s life, including their family dynamics, work, and community environment.
By addressing the whole person, holistic care recognizes that health is influenced by a wide range of factors, including mental health, lifestyle, and social support. This comprehensive approach helps to identify and address the root causes of health issues, rather than merely treating symptoms.
4. Empathy and Compassion
Empathy and compassion are essential components of patient-centered care. These qualities enable healthcare providers to connect with patients on a human level, understanding their fears, anxieties, and hopes. Empathetic care fosters trust and builds a strong therapeutic relationship, which is vital for effective communication and collaboration.
In patient-centered care, providers are encouraged to take the time to listen to patients, validate their feelings, and provide reassurance and support. This compassionate approach not only improves the patient’s experience but also has been shown to enhance clinical outcomes, as patients who feel understood and supported are more likely to engage in their care.
The Secondary Effects of Patient-Centered Care
While the primary focus of patient-centered care is to improve the patient experience and health outcomes, its implementation has broader secondary effects that impact various aspects of the healthcare system. These effects can be observed in areas such as healthcare delivery, provider satisfaction, and overall system efficiency.
1. Improved Patient Satisfaction and Loyalty
One of the most immediate secondary effects of patient-centered care is an increase in patient satisfaction. When patients feel respected, heard, and involved in their care, they are more likely to report higher levels of satisfaction with their healthcare experience. This satisfaction extends beyond individual interactions to include the overall perception of the healthcare system.
Increased patient satisfaction also leads to greater patient loyalty. Patients who have positive experiences with their care are more likely to return to the same providers for future care and to recommend those providers to others. This loyalty can be particularly important in competitive healthcare markets, where patient retention is a key factor in the financial stability of healthcare organizations.
2. Enhanced Provider Satisfaction and Reduced Burnout
Patient-centered care not only benefits patients but also has a positive impact on healthcare providers. By fostering a more collaborative and empathetic approach to care, providers often find greater professional fulfillment in their work. This satisfaction comes from knowing that they are making a meaningful difference in their patients’ lives and from the strong therapeutic relationships that develop as a result of patient-centered care.
Moreover, patient-centered care can help reduce burnout among healthcare providers. Burnout is a significant issue in the healthcare industry, often driven by high workloads, administrative burdens, and a lack of meaningful patient interactions. By prioritizing quality interactions over quantity and by empowering patients to take an active role in their care, patient-centered care can alleviate some of the pressures that contribute to burnout. Providers who feel supported and valued in their roles are more likely to experience job satisfaction and remain engaged in their work.
3. Better Health Outcomes and Reduced Costs
Another important secondary effect of patient-centered care is its impact on health outcomes and healthcare costs. Research has shown that when patients are actively engaged in their care, they are more likely to adhere to treatment plans, manage chronic conditions effectively, and make healthier lifestyle choices. This proactive approach to health can lead to better outcomes, such as lower rates of hospital readmissions, fewer complications, and improved management of chronic diseases.
In addition to improving health outcomes, patient-centered care can also contribute to cost savings. By focusing on prevention, early intervention, and effective management of chronic conditions, this approach can reduce the need for expensive emergency care and hospitalizations. Furthermore, by improving care coordination and communication among providers, patient-centered care can help eliminate redundancies and inefficiencies in the healthcare system, leading to overall cost reductions.
4. Increased Health Equity
Patient-centered care has the potential to address health disparities and promote greater health equity. By recognizing and responding to the unique needs and preferences of each patient, this approach can help reduce barriers to care and ensure that all patients, regardless of their background or circumstances, receive high-quality care.
For example, patient-centered care can improve access to care for underserved populations by addressing cultural, linguistic, and socioeconomic barriers. Healthcare providers who practice patient-centered care are more likely to consider the social determinants of health, such as income, education, and housing, and to tailor their care accordingly. This personalized approach can help bridge the gap between different patient populations and contribute to more equitable health outcomes.
5. Strengthened Patient-Provider Relationships
Finally, one of the most significant secondary effects of patient-centered care is the strengthening of the patient-provider relationship. This relationship is built on trust, communication, and mutual respect, and it is essential for effective care delivery. Strong patient-provider relationships lead to better communication, more accurate diagnoses, and greater adherence to treatment plans.
In a patient-centered care model, the provider is not just a medical expert but also a partner in the patient’s health journey. This partnership fosters a sense of shared responsibility for health outcomes and encourages patients to take an active role in their care. As a result, patients are more likely to feel empowered and confident in managing their health, leading to better overall outcomes.
Conclusion
Patient-centered care represents a transformative approach to healthcare that prioritizes the needs, values, and preferences of patients. By fostering a collaborative and empathetic relationship between patients and providers, this model of care improves patient satisfaction, enhances provider fulfillment, and leads to better health outcomes. The secondary effects of patient-centered care, including reduced costs, increased health equity, and strengthened patient-provider relationships, demonstrate its far-reaching impact on the healthcare system as a whole.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, patient-centered care will remain a crucial guiding principle, ensuring that care delivery is not only effective but also compassionate, respectful, and responsive to the diverse needs of patients. By embracing.